|
|
Post Last Edit by mencacus at 19-6-2011 10:02

Galaksi merupakan kumpulan bintang-bintang yang terdapat dalam Alam Semesta. Galaksi dalam mana sistem suria, iaitu bumi dan matahari berada di dalamnya dikenali sebagai Bima Sakti.
Bintang-bintang sentiasa wujud secara berkelompok yang dikenali sebagai galaksi, bersama-sama dengan gas, debu interstellar, dan "jisim gelap"; sekitar 10-20% dari galaksi terdiri daripada bintang, gas, dan debu. Galaksi dikekalkan bersama oleh tarikan graviti dan komponen galaksi mengorbit satu pusat. Terdapat bukti bahawa lubang gelap mungkin wujud di pusat sebahagian, atau kebanyakan, galaksi. Galaksi terbentuk dari protogalaksi.
Perkataan galaksi dalam bahasa Inggeris galaxy diambil dari nama galaksi kita , Bima Sakti ( Milky Way ), menggunakan perkataan Yunani gala (umumnya galaktos) bererti susu.
Jenis galaksi
Galaksi terdapat dalam tiga bentuk utama: ellipticals, spirals, dan tidak sekata ( irregulars ). Gambaran yang lebih lengkap mengenai jenis-jenis galaksi diberikan oleh aturan Hubble ( Hubble sequence ). Galaksi kita, Bima Sakti, kadang-kala secara ringkas dipanggil Galaksi (dengan huruf besar), adalah barred spiral yang besar sekitar 30 kiloparsecs atau 100,000 tahun cahaya diameter, mengandungi hampir 300 juta bintang dan mempunyai jumlah keseluruhan jisim sekitar satu trillion kali ganda jisim matahari.
Dalam spiral galaksi, the spiral arms mempunyai bentuk bersamaan logarithmic spiral, pola yang boleh dibuktikan secara teorinya hasil dari gangguan dalam jisim bintang berputar secara sekata. Seperti bintang, lengan spiral juga berputar pada satu pusat, tetapi ia berlaku pada angular velocity tetap. Ini bererti bahawa bintang bergerak kedalam dan keluar lengan spiral. Lengan spiral dijangkakan sebagai kawasan kepadatan tinggi atau gelombang kepadatan. Ketika bintang bergerak ke dalam lengan, ia menjadi perlahan, dengan itu menghasilkan kepadatan lebih tinggi; ia menyerupai "gelombang" pergerakan perlahan sepanjang highway yang dipenuhi kereta.
Lengan galaksi jelas kelihatan disebabkan kepadatan tinggi memudahkan pembentukan bintang dan dengan itu ia mempunyai banyak bintang muda dan terang.
Struktur berskala besar
Ruang antara galaksi hampir kosong, kecuali bagi awan gas intergalaktik.
Hanya sebahagian kecil galaksi wujud secara bersendirian; dan ia dikenali sebagai galaksi lapangan ('field Galaksi'). Kebanyakan galaksi terikat oleh daya tarikan graviti dengan beberapa galaksi yang lain. Struktur yang mengandungi sehingga 50 galaksi dipanggil sebagai kelompok galaksi ( groups of galaksi ), dan struktur mengandungi beribu-ribu galaksi terkandung dalam kawasan beberapa megaparsec melintang dikenali sebagai gugusan galaksi. Gugusan super ( Supercluster ) adalah satu kumpulan besar bintang yang mengandungi beribu juta galaksi, dalam gugusan, kelompok, dan kadang-kala bersendirian; sepanjang yang kita ketahui alam sejagat adalah sekata pada skala lebih dari ini.
Galaksi kita merupakan ahli Kumpulan Tempatan ( Local Group ), dan bersama-sama dengan Galaksi Andromeda menguasainya; pada keseluruhannya Kumpulan Tempatan mengandungi sekitar 30 galaksi dalam ruang sekitar ten megaparsecs melintang. Kumpulan Tempatan merupakan sebahagian dari Gugusan super tempatan ( Local Supercluster ), juga dikenali sebagai Virgo Supercluster.
Sumber : wikipedia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Post Last Edit by mencacus at 19-6-2011 10:03
Sejarah
Pada tahun 1610, Galileo Galilei menggunakan teleskop untuk mengkaji jalur terang di langit yang dikenali sebagai Milky Way dan mendapati bahawa ia terdiri daripada bintang malap yang banyak. Dalam treatise pada tahun 1755, Immanuel Kant, menggunakan hasil kerja awal oleh astronomi Thomas Wright, menjangkakan (secara benar) bahawa galaksi terdiri daripada sejumlah besar bintang yang berputar, dikekalkan oleh daya tarikan graviti seumpama dengan sistem suria tetapi pada skala yang lebih besar. Cakera bintang yang terhasil akan dilihat sebagai jalur di langit dari sudut pandangan kita pada kedudukan dalam cakera. Kant juga menjangkakan bahawa sebahagian nebula yang kelihatan di langit mungkin galaksi yang terasing.
Pada akhir abad ke 18, Charles Messier mengumpulkan katalog mengandungi 109 nebulae paling jelas, kemudian diikuti dengan katalog 5000 nebulae dihimpun oleh William Herschel. Pada tahun 1845, Lord Rosse membina teleskop baru dan mampu membezakan antara nebulae elliptical dan spiral nebulae. Dia juga berjaya mengenal pasti sumber titik individu sebahagian dari nebulae ini, menyokong jangkaan Kant yang lebih awal. Bagaimanapun, nebulae tidak diterima umum sebagai galaksi terasing jauh sehingga pekara itu diselesaikan oleh Edwin Hubble pada awal 1920an dengan menggunakan teleskop baru. Dia berjaya menyelesaikan bahagian luar sesetengah spiral nebulae sebagai kumpulan bintang individual dan mengenal pasti sebahagian pengubah Cepheid ( Cepheid variable ), dengan itu membenarkan anggaran mengenai jarak kepada nebulae: ia terlalu jauh untuk menjadi sebahagian Bima Sakti Milky Way. Pada tahun 1936, Hubble menghasilkan sistem pengkelasan untuk Galaksi yang masih digunakan sehingga hari ini, aturan Hubble.
Cubaan pertama menjelaskan bentuk Bima Sakti dan kedudukan matahari di dalamnya dijalankan oleh William Herschel pada tahun 1785 dengan mengira dengan cermat jumlah bintang pada kedudukan berlainan di langit. Menggunakan pendekatan yang lebih baik, Kapteyn pada tahun 1920 arrived at the picture of a small (diameter ~15 kiloparsecs) ellipsoid galaxy with the sun close to the center. Kaedah berlainan digunakan oleh Harlow Shapley berasaskan pengkatalog globular cluster mendorong kepada gambaran berlainan: cakera leper dengan diameter sekitar ~70 kiloparsecs dan matahari jauh dari pusat. Kedua analisa gagal mengambil kira penyerapan cahaya oleh habuk interstellar dust yang hadir dalam galactic plane; apabila Robert Julius Trumpler mengambil kira kesan ini pada 1930 dengan mengkaji open cluster, gambar galaksi kita hari ini seperti digambarkan di atas muncul.
Pada tahun 1944, Hendrik van de Hulst menjangkakan radiasi microwave pada jarak gelombang 21 sentimeter, terhasil dari gas hidrogen atomik interstellar atomic; radiasi ini dikesan pada tahun 1951. Radiasi ini membenarkan kajian mengenai Galaksi yang lebih baik kerana ia tidak terjejas oleh penyerapan debu dan Doppler shiftnya boleh digunakan untuk memetakan pergerakan gas dalam Galaksi. Pemerhatian ini membawa kepada postulation of a rotating bar structure dipusat Galaksi. Dengan teleskop radio yang lebih baik, gas hidrogen boleh dijejak dalam Galaksi lain. Pada tahun 1970-an ia disedari bahawa jumlah keseluruhan jisim yang dapat dilihat (dari bintang dan gas) tidak memberikan kelajuan putaran gas, dengan itu mendorong kepada postulation jisim gelap ( dark matter ).
Bermula pada 1990-an, Teleskop Angkasa Hubble ( Hubble Space Telescope ) menghasilkan pemantauan lebih baik. Antara lain, ia mengesahkan bahawa jisim gelap yang hilang dalam galaksi kita tidak semata-mata terdiri dari bintang kecil yang malap. Ia mengambil gambar Hubble Deep Field, memberikan bukti bahawa dalam alam yang dapat dilihat sahaja, wujudnya beratus juta Galaksi.
Pada tahun 2004, galaksi Abell 1835 IR1916 menjadi galaksi terjauh pernah dilihat manusia.
Sumber : wikipedia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Post Last Edit by mencacus at 19-6-2011 10:04
versi bahasa inggeris
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The name is from the Greek word galaxias [γαλαξίας], literally meaning "milky", a reference to the Milky Way galaxy. Typical galaxies range from dwarfs with as few as ten million (107) stars, up to giants with a hundred trillion (1014) stars, all orbiting the galaxy's center of mass. Galaxies may contain many star systems, star clusters, and various interstellar clouds. The Sun is one of the stars in the Milky Way galaxy; the Solar System includes the Earth and all the other objects that orbit the Sun.
Historically, galaxies have been categorized according to their apparent shape (usually referred to as their visual morphology). A common form is the elliptical galaxy, which has an ellipse-shaped light profile. Spiral galaxies are disk-shaped assemblages with dusty, curving arms. Galaxies with irregular or unusual shapes are known as irregular galaxies, and typically result from disruption by the gravitational pull of neighboring galaxies. Such interactions between nearby galaxies, which may ultimately result in galaxies merging, may induce episodes of significantly increased star formation, producing what is called a starburst galaxy. Small galaxies that lack a coherent structure could also be referred to as irregular galaxies.
There are probably more than 170 billion (1.7 × 1011) galaxies in the observable universe. Most galaxies are 1,000 to 100,000 parsecs in diameter and are usually separated by distances on the order of millions of parsecs (or megaparsecs). Intergalactic space (the space between galaxies) is filled with a tenuous gas of an average density less than one atom per cubic meter. The majority of galaxies are organized into a hierarchy of associations called clusters, which, in turn, can form larger groups called superclusters. These larger structures are generally arranged into sheets and filaments, which surround immense voids in the universe.
Although it is not yet well understood, dark matter appears to account for around 90% of the mass of most galaxies. Observational data suggests that supermassive black holes may exist at the center of many, if not all, galaxies. They are proposed to be the primary cause of active galactic nuclei found at the core of some galaxies. The Milky Way galaxy appears to harbor at least one such object within its nucleus.
Etymology
The word galaxy derives from the Greek term for our own galaxy, galaxias (γαλαξίας), or kyklos galaktikos, meaning "milky circle" for its appearance in the sky. In Greek mythology, Zeus places his son born by a mortal woman, the infant Heracles, on Hera's breast while she is asleep so that the baby will drink her divine milk and will thus become immortal. Hera wakes up while breastfeeding and then realizes she is nursing an unknown baby: she pushes the baby away and a jet of her milk sprays the night sky, producing the faint band of light known as the Milky Way.
In the astronomical literature, the capitalized word 'Galaxy' is used to refer to our galaxy, the Milky Way, to distinguish it from the billions of other galaxies. The term Milky Way first appeared in the English language in a story by Chaucer.
"See yonder, lo, the Galaxyë
Which men clepeth the Milky Wey,
For hit is whyt."
—Geoffrey Chaucer. The House of Fame, c. 1380.
When William Herschel constructed his catalog of deep sky objects in 1786, he used the name spiral nebula for certain objects such as M31. These would later be recognized as immense conglomerations of stars, when the true distance to these objects began to be appreciated, and they would be termed island universes. However, the word Universe was understood to mean the entirety of existence, so this expression fell into disuse and the objects instead became known as galaxies.
Sumber : wikipedia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Post Last Edit by mencacus at 19-6-2011 10:01
Observation history
The realization that we live in a galaxy, and that there were, in fact, many other galaxies, parallels discoveries that were made about the Milky Way and other nebulae in the night sky.
The Milky Way
The Greek philosopher Democritus (450–370 BC) proposed that the bright band on the night sky known as the Milky Way might consist of distant stars. Aristotle (384–322 BC), however, believed the Milky Way to be caused by "the ignition of the fiery exhalation of some stars which were large, numerous and close together" and that the "ignition takes place in the upper part of the atmosphere, in the region of the world which is continuous with the heavenly motions." The Neoplatonist philosopher Olympiodorus the Younger (c. 495–570 AD) criticized this view, arguing that if the Milky Way were sublunary it should appear different at different times and places on the Earth, and that it should have parallax, which it does not. In his view, the Milky Way was celestial. This idea would be influential later in the Islamic world.
The Arabian astronomer, Alhazen (965–1037), made the first attempt at observing and measuring the Milky Way's parallax, and he thus "determined that because the Milky Way had no parallax, it was very remote from the Earth and did not belong to the atmosphere." The Persian astronomer Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī (973–1048) proposed the Milky Way galaxy to be "a collection of countless fragments of the nature of nebulous stars." The Andalusian astronomer Ibn Bajjah ("Avempace", d. 1138) proposed that the Milky Way was made up of many stars that almost touch one another and appear to be a continuous image due to the effect of refraction from sublunary material, citing his observation of the conjunction of Jupiter and Mars as evidence of this occurring when two objects are near. The Syrian-born Ibn Qayyim Al-Jawziyya (1292–1350) proposed the Milky Way galaxy to be "a myriad of tiny stars packed together in the sphere of the fixed stars".
Actual proof of the Milky Way consisting of many stars came in 1610 when Galileo Galilei used a telescope to study the Milky Way and discovered that it is composed of a huge number of faint stars. In 1750 Thomas Wright, in his An original theory or new hypothesis of the Universe, speculated (correctly) that the galaxy might be a rotating body of a huge number of stars held together by gravitational forces, akin to the solar system but on a much larger scale. The resulting disk of stars can be seen as a band on the sky from our perspective inside the disk. In a treatise in 1755, Immanuel Kant elaborated on Wright's idea about the structure of the Milky Way.
The first attempt to describe the shape of the Milky Way and the position of the Sun in it was carried out by William Herschel in 1785 by carefully counting the number of stars in different regions of the sky. He produced a diagram of the shape of the galaxy with the solar system close to the center. Using a refined approach, Kapteyn in 1920 arrived at the picture of a small (diameter about 15 kiloparsecs) ellipsoid galaxy with the Sun close to the center. A different method by Harlow Shapley based on the cataloguing of globular clusters led to a radically different picture: a flat disk with diameter approximately 70 kiloparsecs and the Sun far from the center. Both analyses failed to take into account the absorption of light by interstellar dust present in the galactic plane, but after Robert Julius Trumpler quantified this effect in 1930 by studying open clusters, the present picture of our galaxy, the Milky Way, emerged.

Galactic Center of the Milky Way
Sumber : wikipedia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Post Last Edit by mencacus at 19-6-2011 10:10
Distinction from other nebulae
In the 10th century, the Persian astronomer, Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi (known in the West as Azophi), made the earliest recorded observation of the Andromeda Galaxy, describing it as a "small cloud". Al-Sufi also identified the Large Magellanic Cloud, which is visible from Yemen, though not from Isfahan; it was not seen by Europeans until Magellan's voyage in the 16th century. These were the first galaxies other than the Milky Way to be observed from Earth. Al-Sufi published his findings in his Book of Fixed Stars in 964.
In 1750 Thomas Wright, in his An original theory or new hypothesis of the Universe, speculated (correctly) that Milky Way was a flattened disk of stars, and that some of the nebulae visible in the night sky might be separate Milky Ways. In 1755 Immanuel Kant introduced the term "island universe" for these distant nebulae.
Toward the end of the 18th century, Charles Messier compiled a catalog containing the 109 brightest nebulae (celestial objects with a nebulous appearance), later followed by a larger catalog of 5,000 nebulae assembled by William Herschel. In 1845, Lord Rosse constructed a new telescope and was able to distinguish between elliptical and spiral nebulae. He also managed to make out individual point sources in some of these nebulae, lending credence to Kant's earlier conjecture.
In 1912, Vesto Slipher made spectrographic studies of the brightest spiral nebulae to determine if they were made from chemicals that would be expected in a planetary system. However, Slipher discovered that the spiral nebulae had high red shifts, indicating that they were moving away at rate higher than the Milky Way's escape velocity. Thus they were not gravitationally bound to the Milky Way, and were unlikely to be a part of the galaxy.
In 1917, Heber Curtis had observed a nova S Andromedae within the "Great Andromeda Nebula" (Messier object M31). Searching the photographic record, he found 11 more novae. Curtis noticed that these novae were, on average, 10 magnitudes fainter than those that occurred within our galaxy. As a result he was able to come up with a distance estimate of 150,000 parsecs. He became a proponent of the so-called "island universes" hypothesis, which holds that spiral nebulae are actually independent galaxies.

Sketch of the Whirlpool Galaxy by Lord Rosse in 1845
In 1920 the so-called Great Debate took place between Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis, concerning the nature of the Milky Way, spiral nebulae, and the dimensions of the Universe. To support his claim that the Great Andromeda Nebula was an external galaxy, Curtis noted the appearance of dark lanes resembling the dust clouds in the Milky Way, as well as the significant Doppler shift.
The matter was conclusively settled in the early 1920s. In 1922, astronomer Ernst Öpik gave a distance determination which supported the theory that the Andromeda Nebula is indeed a distant extra-galactic object. Using the new 100 inch Mt. Wilson telescope, Edwin Hubble was able to resolve the outer parts of some spiral nebulae as collections of individual stars and identified some Cepheid variables, thus allowing him to estimate the distance to the nebulae: they were far too distant to be part of the Milky Way. In 1936 Hubble produced a classification system for galaxies that is used to this day, the Hubble sequence.

Photograph of the "Great Andromeda Nebula" from 1899, later identified as the Andromeda Galaxy
Sumber : wikipedia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Post Last Edit by mencacus at 19-6-2011 10:14
Modern research
In 1944, Hendrik van de Hulst predicted microwave radiation at a wavelength of 21 cm resulting from interstellar atomic hydrogen gas; this radiation was observed in 1951. The radiation allowed for much improved study of the Milky Way Galaxy, since it is not affected by dust absorption and its Doppler shift can be used to map the motion of the gas in the Galaxy. These observations led to the postulation of a rotating bar structure in the center of the Galaxy. With improved radio telescopes, hydrogen gas could also be traced in other galaxies.
In the 1970s it was discovered in Vera Rubin's study of the rotation speed of gas in galaxies that the total visible mass (from the stars and gas) does not properly account for the speed of the rotating gas. This galaxy rotation problem is thought to be explained by the presence of large quantities of unseen dark matter.
Beginning in the 1990s, the Hubble Space Telescope yielded improved observations. Among other things, it established that the missing dark matter in our galaxy cannot solely consist of inherently faint and small stars. The Hubble Deep Field, an extremely long exposure of a relatively empty part of the sky, provided evidence that there are about 125 billion (1.25×1011
) galaxies in the universe. Improved technology in detecting the spectra invisible to humans (radio telescopes, infrared cameras, and x-ray telescopes) allow detection of other galaxies that are not detected by Hubble. Particularly, galaxy surveys in the Zone of Avoidance (the region of the sky blocked by the Milky Way) have revealed a number of new galaxies.
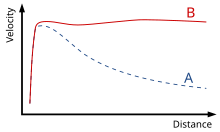
Rotation curve of a typical spiral galaxy: predicted (A) and observed (B). The distance is from the galactic core.

The most distant galaxy: UDFy-38135539
Sumber : wikipedia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Post Last Edit by mencacus at 19-6-2011 10:18
Types and morphology
Galaxies come in three main types: ellipticals, spirals, and irregulars. A slightly more extensive description of galaxy types based on their appearance is given by the Hubble sequence. Since the Hubble sequence is entirely based upon visual morphological type, it may miss certain important characteristics of galaxies such as star formation rate (in starburst galaxies) and activity in the core (in active galaxies).
Ellipticals
The Hubble classification system rates elliptical galaxies on the basis of their ellipticity, ranging from E0, being nearly spherical, up to E7, which is highly elongated. These galaxies have an ellipsoidal profile, giving them an elliptical appearance regardless of the viewing angle. Their appearance shows little structure and they typically have relatively little interstellar matter. Consequently these galaxies also have a low portion of open clusters and a reduced rate of new star formation. Instead they are dominated by generally older, more evolved stars that are orbiting the common center of gravity in random directions. In this sense they have some similarity to the much smaller globular clusters.
The largest galaxies are giant ellipticals. Many elliptical galaxies are believed to form due to the interaction of galaxies, resulting in a collision and merger. They can grow to enormous sizes (compared to spiral galaxies, for example), and giant elliptical galaxies are often found near the core of large galaxy clusters.[50] Starburst galaxies are the result of such a galactic collision that can result in the formation of an elliptical galaxy.
Spirals
Spiral galaxies consist of a rotating disk of stars and interstellar medium, along with a central bulge of generally older stars. Extending outward from the bulge are relatively bright arms. In the Hubble classification scheme, spiral galaxies are listed as type S, followed by a letter (a, b, or c) that indicates the degree of tightness of the spiral arms and the size of the central bulge. An Sa galaxy has tightly wound, poorly defined arms and possesses a relatively large core region. At the other extreme, an Sc galaxy has open, well-defined arms and a small core region. A galaxy with poorly defined arms is sometimes referred to as a flocculent spiral galaxy; in contrast to the grand design spiral galaxy that has prominent and well-defined spiral arms.
In spiral galaxies, the spiral arms do have the shape of approximate logarithmic spirals, a pattern that can be theoretically shown to result from a disturbance in a uniformly rotating mass of stars. Like the stars, the spiral arms rotate around the center, but they do so with constant angular velocity. The spiral arms are thought to be areas of high density matter, or "density waves". As stars move through an arm, the space velocity of each stellar system is modified by the gravitational force of the higher density. (The velocity returns to normal after the stars depart on the other side of the arm.) This effect is akin to a "wave" of slowdowns moving along a highway full of moving cars. The arms are visible because the high density facilitates star formation, and therefore they harbor many bright and young stars.
A majority of spiral galaxies have a linear, bar-shaped band of stars that extends outward to either side of the core, then merges into the spiral arm structure. In the Hubble classification scheme, these are designated by an SB, followed by a lower-case letter (a, b or c) that indicates the form of the spiral arms (in the same manner as the categorization of normal spiral galaxies). Bars are thought to be temporary structures that can occur as a result of a density wave radiating outward from the core, or else due to a tidal interaction with another galaxy. Many barred spiral galaxies are active, possibly as a result of gas being channeled into the core along the arms.
Our own galaxy is a large disk-shaped barred-spiral galaxy about 30 kiloparsecs in diameter and a kiloparsec in thickness. It contains about two hundred billion (2×1011) stars and has a total mass of about six hundred billion (6×1011) times the mass of the Sun.

Types of galaxies according to the Hubble classification scheme. An E indicates a type of elliptical galaxy; an S is a spiral; and SB is a barred-spiral galaxy.

The Whirlpool Galaxy (on left), an example of an unbarred spiral galaxy.

NGC 1300, an example of a barred spiral galaxy.
Sumber : wikipedia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Post Last Edit by mencacus at 19-6-2011 10:22
Other morphologies
Peculiar galaxies are galactic formations that develop unusual properties due to tidal interactions with other galaxies. An example of this is the ring galaxy, which possesses a ring-like structure of stars and interstellar medium surrounding a bare core. A ring galaxy is thought to occur when a smaller galaxy passes through the core of a spiral galaxy. Such an event may have affected the Andromeda Galaxy, as it displays a multi-ring-like structure when viewed in infrared radiation.
A lenticular galaxy is an intermediate form that has properties of both elliptical and spiral galaxies. These are categorized as Hubble type S0, and they possess ill-defined spiral arms with an elliptical halo of stars. (Barred lenticular galaxies receive Hubble classification SB0.)
In addition to the classifications mentioned above, there are a number of galaxies that can not be readily classified into an elliptical or spiral morphology. These are categorized as irregular galaxies. An Irr-I galaxy has some structure but does not align cleanly with the Hubble classification scheme. Irr-II galaxies do not possess any structure that resembles a Hubble classification, and may have been disrupted. Nearby examples of (dwarf) irregular galaxies include the Magellanic Clouds.
Dwarfs
Despite the prominence of large elliptical and spiral galaxies, most galaxies in the universe appear to be dwarf galaxies. These galaxies are relatively small when compared with other galactic formations, being about one hundredth the size of the Milky Way, containing only a few billion stars. Ultra-compact dwarf galaxies have recently been discovered that are only 100 parsecs across.
Many dwarf galaxies may orbit a single larger galaxy; the Milky Way has at least a dozen such satellites, with an estimated 300–500 yet to be discovered. Dwarf galaxies may also be classified as elliptical, spiral, or irregular. Since small dwarf ellipticals bear little resemblance to large ellipticals, they are often called dwarf spheroidal galaxies instead.
A study of 27 Milky Way neighbors found that dwarf galaxies were all approximately 10 million solar masses, regardless of whether they have thousands or millions of stars. This has led to the suggestion that galaxies are largely formed by dark matter, and that the minimum size may indicate a form of warm dark matter incapable of gravitational coalescence on a smaller scale.

Hoag's Object, an example of a ring galaxy.

NGC 5866, an example of a lenticular galaxy.
Sumber : wikipedia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bnyknye........... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pandora letak kat galaxy yang mana satu??  |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pandora letak kat galaxy yang mana satu??
HaMiZiE Post at 22-5-2011 00:07 
kapal angkasa x lepas dari bima sakti .....nak ke andromeda yang dekat tu pun x sampai ..... so kat dalam bima sakti lah ...... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
kalo manusia leh mencipta space craft selaju cahaya pun... still take times kalo nak travel dari satu galaxy to another galaxy...
sedangkan dasar lautan yang luas kat bumi pun tak terexplore... nie kan pula universe yang teramat luas nieee.....  |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
kalo manusia leh mencipta space craft selaju cahaya pun... still take times kalo nak travel dari sat ...
HaMiZiE Post at 22-5-2011 00:24 
bayangkan dari hujung bimasakti ke hujung bimasakti lebarnya 100,000 tahun cahaya ..... boleh sampai ke kita ke andromeda tu yang jaraknya 3 juta tahun cahaya ? ...... luas sungguh alam ciptaan Allah nie ...... ( purata umur manusia pun 75 tahun ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
memang luas... ciptaan Allah...
kalo manosia ni dibandingkan ngan universe... betapa kerdiln ...
HaMiZiE Post at 22-5-2011 00:48 
dalam anggaran , jumlah bintang di bima sakti adalah 300 juta buah ....... matahari mempunyai 12 buah planet ( kajian NASA ) ..... kita kalikan 12 buah planet dengan 300 juta buah bintang ( teori sahaja ) adalah 3.6 billion planet ...... belum lagi diorang kata kat bimasakti nie ada 1 billion bintang ..... banyak tu .....
tak kira lagi dengan galaksi2 yang lain ..... dianggarkan galaksi andromeda 3 kali ganda saiz bimasakti ..... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tq 4 d info |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pernah tgk satu dokumentari kat National Geo Channel kalo tak silap ttg 'Journey to the edge o ...
HaMiZiE Post at 22-5-2011 11:22 
best nye u dapat tengok dokumentari nie |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
best nye u dapat tengok dokumentari nie
areenarena Post at 23-5-2011 22:28 
memang best dokumentari tue...
ala.. kalo dah nama astro.. pasti akan ada ulang tayang tu nanti... bukan sekali... banyak kaliiiiii 
just stick to learning channel (luper ar channel mana yang tayangkan dokumentari nie)... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
memang best dokumentari tue...
ala.. kalo dah nama astro.. pasti akan ada ulang tayang tu nan ...
HaMiZiE Post at 23-5-2011 22:37 
tau xpe |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Category: Belia & Informasi
|